Sun Facts
Over the course of human history the Sun has been feared and worshipped. Rightfully so. What our ancestors knew on a fundamental level was that the Sun provides a vital ingredient for most of the life on Earth. Without the energy provided through sunlight, vegetation cannot grow, and without vegetation animals do not have a source of nourishment. However, what we know today that our ancestors did not is just how far reaching the scope of the Sun's influence is.
As our scientific knowledge has increased so too has our understanding that the Earth is merely a piece in the larger structure we know as the Solar System. What we have also discovered is that although other planets and bodies in the Solar System may not possess life, the Sun is just as influential to them.
What is the Sun?
The Sun is what is known as a main sequence star; that is, a sphere composed primarily of the two gases hydrogen and helium such that certain conditions are met. The first condition is that it must have a mass falling within a certain range. Though debated, this range is generally accepted to be between approximately 1.4 x 1029 kg and 3.0 x 1032 kg. (This range is often describe as at least 75 times the mass of Jupiter and no more than 150 times the mass of the Sun itself.) The second and most important condition is that nuclear fusion must be present. Nuclear fusion is the process whereby two lighter atomic nuclei join or “fuse” together to produce a heavier atomic nucleus. In the context of stars, hydrogen is the lighter and helium the heavier.
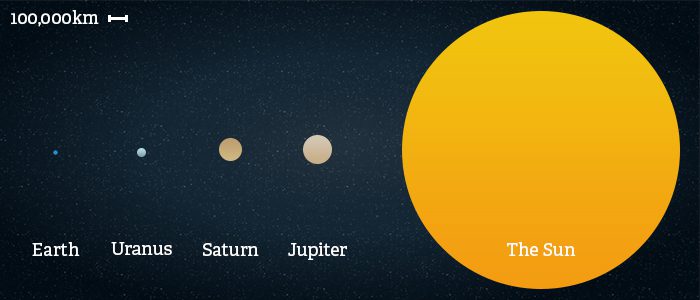
Size of the Sun
The size of the Sun compared to the largest known stars (red giants) is not very big. However, if compared to the most common type of star in the universe, the red dwarf, the Sun is quite a bit larger. Thus, the Sun is not the biggest type of star in the universe, but it is definitely larger than most.
As far as the Sun’s mass compared to other bodies found in our solar system, the Sun is easily the most massive. The Sun alone contains 99.8% of the total mass in the Solar System.
In terms of size, the Sun has a diameter of roughly 1.4 million kilometers (870,000 miles). To put this in perspective, this is almost 110 times the diameter of the Earth. What this means is that about one million Earth’s could fit inside the Sun.
Facts about the Sun
- The Sun accounts for 99.86% of the mass in the solar system. It has a mass of around 330,000 times that of Earth. It is three quarters hydrogen and most of its remaining mass is helium.
- Over one million Earth’s could fit inside the Sun. If you were to fill a hollow Sun with spherical Earths, somewhere around 960,000 would fit inside. However, if you squashed those Earths to ensure there was no wasted space then you could fit 1,300,000 Earths inside the Sun. The surface area of the Sun is 11,990 times that of Earth.
- One day the Sun will consume the Earth. The Sun will continue to burn for about 130 million years after it burns through all of its hydrogen, instead burning helium. During this time it will expand to such a size that it will engulf Mercury, Venus, and Earth. When it reaches this point, it will have become a red giant star.
- The energy created by the Sun’s core is nuclear fusion. This huge amount of energy is produced when four hydrogen nuclei are combined into one helium nucleus.
- The Sun is almost a perfect sphere. Considering the sheer size of the Sun, there is only a 10 km difference in its polar and equatorial diameters – this makes it the closest thing to a perfect sphere observed in nature.
- The Sun is travelling at 220 km per second. It is around 24,000-26,000 light-years from the galactic centre and it takes the Sun approximately 225-250 million years to complete one orbit of the centre of the Milky Way.
- The Sun will eventually be about the size of Earth. Once the Sun has completed its red giant phase, it will collapse. It’s huge mass will be retained, but it will have a volume similar to that of Earth. When that happens, it will be known as a white dwarf.
- It takes eight minutes for light reach Earth from the Sun. The average distance from the Sun to the Earth is about 150 million km. Light travels at 300,000 km per second so dividing one by the other gives you 500 seconds – eight minutes and twenty seconds. This energy can reach Earth in mere minutes, but it takes millions of years to travel from the Sun’s core to its surface.
- The Sun is halfway through its life. At 4.5 billion years old, the Sun has burned off around half of its hydrogen stores and has enough left to continue burning hydrogen for another 5 billion years. Currently the Sun is a yellow dwarf star.
- The distance between Earth and Sun changes. This is because the Earth travels on a elliptical orbit path around the Sun. The distance between the two ranges from 147 to 152 million km. This distance between them is one Astronomical Unit (AU).
- The Sun rotates in the opposite direction to Earth with the Sun rotating from west to east instead of east to west like Earth.
- The Sun rotates more quickly at its equator than it does close to its poles. This is known as differential rotation.
- The Sun has a powerful magnetic field. When magnetic energy is released by the Sun during magnetic storms, solar flares occur which we see on Earth as sunspots. Sunspots are dark areas on the Sun’s surface caused by magnetic variations. The reason they appear dark is due to their temperature being much lower than surrounding areas.
- Temperatures inside the Sun can reach 15 million degrees Celsius. Energy is generated through nuclear fusion in the Sun’s core – this is when hydrogen converts to helium – and because objects generally expand, the Sun would explode like an enormous bomb if it wasn’t for it’s tremendous gravitational pull.
- The Sun generates solar winds. These are ejections of plasma (extremely hot charged particles) that originate in the layer of the Sun know as the corona and they can travel through the solar system at up to 450 km per second.
- The atmosphere of the Sun is composed of three layers: the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona.
- The Sun is classified as a yellow dwarf star. It is a main sequence star with surface temperatures between 5,000 and 5,700 degrees celsius (9,000 and 10,300 degrees fahrenheit).
- The Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis are caused by the interaction of solar winds with Earth’s atmosphere.
What type of star is the Sun?
Although we think of our Sun as a unique celestial body, it is, in fact, one of trillions of stars in the universe. On top of this, the Sun is rather ordinary as far as stars go. The official classification for our Sun is G V star (often referred to as a Yellow Dwarf star), which means that it is a main sequence star whose surface temperature is between 5027°C and 5727°C.
Some estimates for stars similar to the Sun in the Milky Way galaxy alone are as high as 7 billion. If this number is correct, there could be over one trillion stars that are roughly the same as our Sun in the universe.
Does the Sun have another name?
While our Sun does not have an official scientific name, it does have another common name: Sol. This name originates from the ancient Roman’s god of the Sun, Sol. This alternate name is where we get the term “solar system,” which literally means system of the Sun.


